New USCIS data reveals a historic crackdown under the Trump administration, with over 14,000 cases referred to ICE, 182 confirmed national security risks, and a record-breaking 196,000 Notices to Appear issued in 2025. Learn about the stricter citizenship tests, neighborhood checks, and the “America First” approach reshaping US immigration.
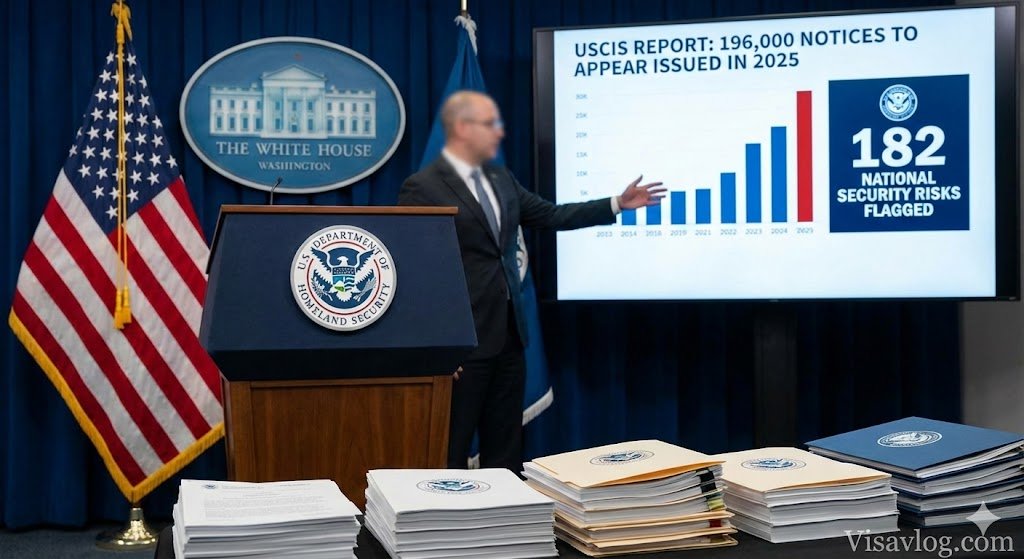
The United States Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) has released comprehensive new figures that underscore the sheer scale of the Trump administration’s immigration crackdown during its first year back in the White House. The data paints a picture of an agency radically transformed to prioritize national security and fraud detection over benefit adjudication. According to the report, USCIS has referred more than 14,000 specific immigration cases to Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) due to serious national security and fraud concerns. Among these rigorous screenings, the agency flagged 182 individuals as confirmed or suspected national security risks, a statistic that officials are citing as justification for the extreme vetting measures currently being implemented.
This “America First” approach has fundamentally altered the landscape for foreign nationals in the United States. The administration’s strategy is not limited to border enforcement but extends deep into the interior adjudication process. One of the most significant metrics released is the issuance of a record-breaking 196,000 Notices to Appear (NTAs), effectively placing nearly two hundred thousand migrants into formal removal proceedings. This surge in enforcement activity aligns with broader trends where ICE Enforcement Arrests have seen a dramatic uptick, targeting not just those with criminal records but also individuals with visa violations that might have been overlooked in previous administrations.
- Read More
- US Suspends Green Card Lottery (Diversity Visa) Indefinitely Following Brown University & MIT Shootings
- Trump Expands Travel Ban to 39 Countries: The Complete List and Official Reasons
- Harder Than Ever: The Challenges of Being an Immigrant in the USA in 2026
- USA ICE Has Arrested 75,000 Foreigners With No Criminal Records
- Trump Administration Launches Full-Scale Review of Green Cards From 19 Nations
The Return of “Neighborhood Checks” and Enhanced Vetting
In a move that signals a return to post-9/11 era vigilance, the administration has resurrected “neighborhood checks” for citizenship applicants—a practice largely abandoned since the George W. Bush administration. This policy involves immigration officers conducting physical field visits to the neighborhoods of applicants to verify residence and lifestyle claims. This resurrection of on-the-ground surveillance is part of a wider net cast by the Fraud Detection and National Security Directorate (FDNS), which completed 19,300 fraud cases in the last year alone. The agency reported identifying fraud in approximately 65% of the cases it reviewed, a startlingly high percentage that has fueled the government’s argument for stricter scrutiny.
These on-site investigations are coupled with digital surveillance. FDNS officers conducted over 19,500 social media checks, scrutinizing the online footprints of potential immigrants for anti-American sentiment or evidence of fraud. This digital vetting is becoming a standard hurdle, contributing to the US Immigration Challenges 2026 that legal immigrants now face. The message from USCIS Director Joseph B. Edlow was unequivocal: the agency is “restoring order” and prioritizing the safety of Americans over the interests of foreign nationals.
Stricter Citizenship Tests and Fraud Detection
For those seeking naturalization, the path to becoming an American citizen has become significantly steeper. In September, the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) overhauled the citizenship civics test, making it longer and more complex. The total bank of questions was raised from 100 to 128, and the number of questions asked during the interview doubled from 10 to 20. Furthermore, the passing score was increased, requiring applicants to answer 12 questions correctly rather than the previous six. This change aims to ensure a “deeper understanding” of U.S. history and values but effectively serves as a filter that could reduce the number of naturalized citizens.
The crackdown has also been reactive to specific security incidents. Following a violent attack in Washington, D.C., involving an Afghan national, the agency froze asylum processing for all countries and initiated a massive Green Card Security Review. This re-examination of residency permits for nationals from high-risk countries demonstrates the administration’s willingness to retroactively apply security standards. This incident also served as a catalyst for policy shifts that resemble a Green Card Lottery Suspension, halting programs that the administration views as vulnerabilities in the national defense shield.
Recruiting “Homeland Defenders”
To sustain this high level of enforcement, USCIS and DHS have launched aggressive hiring campaigns. Moving away from the terminology of “immigration services officers,” the agency now refers to these roles as “Homeland Defenders,” a title that explicitly reframes the job as a security function rather than an administrative one. The response to these job openings has been robust, with more than 50,000 individuals applying to join USCIS in these new roles. This staffing surge is intended to clear backlogs in fraud detection and ensure that the new, more labor-intensive vetting procedures do not grind the system to a complete halt, although processing times for routine benefits remain high.
The department’s leadership, including DHS Secretary Kristi Noem, has framed these actions as the fulfillment of campaign promises to reverse the “flawed immigration policies” of the Biden era. The administration touts the security of the border and the interior arrests as historic achievements. However, for immigrant communities, the atmosphere is one of heightened anxiety. The expansion of restrictive policies, potentially including a Trump Travel Ban Expansion to additional nations, looms large over families waiting for reunification or visa approvals.
The Broader Impact on Legal Immigration
While much of the rhetoric focuses on illegal immigration, the data shows a clear bleed-over into legal immigration processes. The increased denial rates, the enhanced Request for Evidence (RFE) issuance, and the scrutiny on H-1B and student visas indicate a “merit-based” system that is exceptionally hard to satisfy. The 182 national security risks identified are a small fraction of the millions of applications processed, yet they drive the policy for everyone. The 196,000 Notices to Appear include individuals who may have fallen out of status due to bureaucratic delays or minor technicalities, highlighting how the “zero tolerance” philosophy is applied indiscriminately.
As the administration moves into the next phase of its term, the distinction between “enforcement” and “adjudication” continues to blur. With thousands of arrests made directly at USCIS field offices—venues previously considered safe neutral grounds for interviews—immigrants are now wary of attending their own appointments. This chilling effect is likely to reduce the number of people applying for benefits they are legally entitled to, which, critics argue, may be the unspoken goal of the “America First” immigration agenda.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does the record issuance of 196,000 Notices to Appear (NTAs) mean for migrants?
The issuance of 196,000 Notices to Appear (NTAs) represents a historic high in immigration enforcement activity. An NTA is the formal charging document that initiates deportation proceedings in immigration court. This surge indicates that USCIS is moving aggressively to place individuals into removal proceedings immediately after denying their benefits, rather than simply leaving them without status, signaling a zero-tolerance approach to enforcement.
Why has the Trump administration reinstated “Neighborhood Checks” for applicants?
The administration has brought back “Neighborhood Checks” to rigorously verify the residency and lifestyle claims of immigration applicants. Officers from the Fraud Detection and National Security Directorate (FDNS) physically visit neighborhoods to interview neighbors and observe the applicant’s home. This is intended to root out marriage fraud and ensure that benefits are only granted to those who truthfully reside where they claim.
What specific changes have been made to the U.S. citizenship test in 2025?
The citizenship civics test has been overhauled to be significantly more difficult. The total pool of questions was increased from 100 to 128, and the number of questions asked during the interview doubled from 10 to 20. Additionally, the passing score was raised, requiring applicants to answer 12 questions correctly instead of 6. The questions now also require more nuanced and complex answers regarding U.S. history and values.
Why was asylum processing frozen for all countries?
Asylum processing was suspended globally following a severe security incident in Washington, D.C., involving an Afghan national. The administration used this event as the basis for a comprehensive security review, freezing all new asylum adjudications to re-evaluate vetting protocols. This pause allows the Department of Homeland Security to cross-reference applicants against updated terror watchlists and implement stricter screening measures.
Who are the “Homeland Defenders” mentioned in the new reports?
“Homeland Defenders” is the new official title for USCIS immigration services officers, reflecting a rebranding effort by the administration. This title shift emphasizes the role of these officers as security enforcers rather than just benefit adjudicators. It coincides with a massive hiring campaign of 50,000 new staff members who are being trained to prioritize fraud detection and national security over the rapid processing of applications.
How are social media checks being used in the immigration process?
USCIS is conducting mandatory and extensive reviews of applicants’ public social media profiles. In the past year, over 19,500 such checks were completed to identify inconsistencies, unauthorized employment, or anti-American sentiment. Information found online is frequently used as evidence to deny visas and green cards if it contradicts the formal application or raises any security concerns.
What impact does the identification of 182 national security risks have on policy?
The confirmed identification of 182 national security risks is being used by the administration to justify “extreme vetting